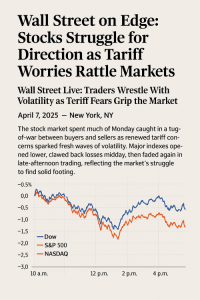
Carbon tax: How much is it to blame for spiking food costs in Canada?

Carbon tax: How much is it to blame for spiking food costs in Canada?
Canada’s carbon tax is a price on carbon pollution that was first implemented in 2019. The tax is currently set at $30 per tonne of carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) and is scheduled to increase to $50 per tonne by 2023.
The carbon tax is designed to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and help Canada meet its climate change goals. However, some critics argue that the tax is driving up food prices.
How much of a role is the carbon tax playing in spiking food costs in Canada? The answer is complex.
On the one hand, the carbon tax does add some cost to food production and transportation. For example, farmers may have to pay more for fuel to operate their machinery, and food processors may have to pay more to heat their facilities.
On the other hand, the carbon tax is also rebated to Canadians on their income taxes. This means that for most people, the carbon tax does not have a significant impact on their overall spending.
In addition, the carbon tax is exempt from food itself. This means that the tax does not directly impact the price of groceries.
However, the carbon tax can indirectly impact food prices. For example, if the cost of transportation increases due to the carbon tax, this can lead to higher food prices.
Overall, the impact of the carbon tax on food prices is relatively modest. A 2020 study by the Bank of Canada estimated that the carbon tax adds about 0.15 percentage points to inflation. This means that the carbon tax is responsible for about 1.5% of the recent increase in food prices.
While the carbon tax is not the main driver of spiking food costs, it is a contributing factor. Other factors, such as supply chain disruptions and the war in Ukraine, are playing a larger role.
What can Canadians do to reduce the impact of the carbon tax on their food budget?
There are a few things that Canadians can do to reduce the impact of the carbon tax on their food budget:
- Buy local food whenever possible. This reduces the distance that food has to travel, which can save on transportation costs.
- Eat less meat. Meat production is a major source of greenhouse gas emissions. By eating less meat, Canadians can help to reduce the overall cost of food production.
- Grow their own food. This is a great way to reduce food costs and avoid the carbon tax altogether.
It is important to note that the carbon tax is a necessary step in addressing climate change. The tax is helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and make Canada’s economy more sustainable.
However, the government should also be taking steps to help Canadians afford food, such as providing rebates to low-income households.